Strength Training for Weight Loss

If your goal is lasting weight loss, strength training is your most powerful tool—more effective than cardio, more sustainable than crash diets, and better for your health than either alone. Yet most people trying to lose weight spend hours on treadmills while avoiding the weight room. Here's the truth: when you lose weight through diet and cardio alone, up to 30% of what you lose can be muscle. Strength training changes this equation, helping you lose primarily fat while preserving or even building the muscle that keeps your metabolism elevated. This program is designed to maximize fat burning, build functional muscle, and create the lean, strong physique you're working toward.
Why Strength Training Beats Cardio for Weight Loss
The traditional approach to weight loss—eat less, do more cardio—has a fundamental problem. Your body adapts to caloric restriction by slowing your metabolism, and cardio accelerates muscle loss. The result? You lose weight initially, but hit plateaus, feel exhausted, and often regain everything (plus more) when you return to normal eating.
Strength training solves this problem through multiple mechanisms. First, muscle is metabolically active—each pound burns roughly 6 calories per day at rest, compared to 2 calories for fat. Building even 5 pounds of muscle increases your daily burn by 20+ calories without any extra effort.
Second, strength training creates an "afterburn effect" (excess post-exercise oxygen consumption, or EPOC) that elevates your metabolism for 24-48 hours after training. A heavy lifting session can burn hundreds of extra calories over the following days.
Finally, strength training preferentially targets fat loss. When combined with adequate protein intake, your body has a reason to preserve muscle while burning fat for fuel. This leads to lasting changes in body composition rather than just numbers on a scale.
Benefits of Strength Training for Weight Loss
Elevated Metabolism
Building muscle increases your basal metabolic rate, meaning you burn more calories even while sleeping and sitting.
Preserved Muscle During Deficit
When eating in a caloric deficit, strength training signals your body to retain muscle and burn fat for fuel instead.
The Afterburn Effect
Intense strength training keeps your metabolism elevated for up to 48 hours post-workout, burning hundreds of extra calories.
Improved Body Composition
Even if the scale doesn't move, you can dramatically change how you look by losing fat and gaining muscle.
Better Insulin Sensitivity
Muscle helps regulate blood sugar, making it easier for your body to use food for energy rather than storing it as fat.
Sustainable Results
Unlike extreme cardio or restrictive diets, strength training builds habits and a body that maintains results long-term.
Increased Energy
As you get stronger, daily activities become easier, leaving more energy for workouts and active recreation.
Program Overview
Who it's for: Anyone focused on fat loss while building or maintaining lean muscle
Don't have all this equipment? GymFriend can build you a custom program using whatever you have available.
Why These Exercises?
Each exercise in this program was selected for a specific reason. Here's why:
Barbell Full Squat
The squat recruits more muscle mass than almost any other exercise, creating massive caloric demand and metabolic stimulus.
Barbell Deadlift
Deadlifts work the entire posterior chain and core, building strength while burning significant calories.
Barbell Bench Press
A compound pushing movement that builds the chest, shoulders, and triceps while elevating metabolism.
Barbell Bent Over Row
Builds upper back and bicep strength while improving posture—critical for those who sit at desks.
Dumbbell Lunge
Unilateral leg work that builds balance and hits the quads and glutes hard.
Smith Standing Military Press
Overhead pressing builds shoulder strength and requires full-body stabilization, maximizing caloric burn.
Pull-up
The ultimate upper body exercise for building a strong back and arms using your body weight.
Weighted Front Plank
Core stability is essential for safe lifting and maintaining good posture as you lose weight.
The Complete 3 days Program
Follow this program consistently for best results. Start with weights that feel manageable and aim to increase gradually each week as you get stronger.
Want this program adjusted for your fitness level, goals, or schedule? GymFriend can create a personalized version just for you.
Maximizing Your Results
- Pair this program with a moderate caloric deficit (300-500 calories below maintenance). Extreme deficits will compromise your strength gains.
- Prioritize protein—aim for 0.8-1g per pound of body weight to preserve muscle while losing fat.
- Keep rest periods short (60-90 seconds) to maintain elevated heart rate and maximize caloric burn.
- Track your measurements and progress photos, not just the scale. Muscle gain can mask fat loss on the scale.
- Get 7-8 hours of sleep. Sleep deprivation increases hunger hormones and decreases fat loss.
- Add 2-3 sessions of low-intensity cardio (walking, cycling) on non-lifting days for additional calorie burn without compromising recovery.
- Stay consistent—sustainable fat loss happens at 0.5-1% of body weight per week. Faster isn't better.
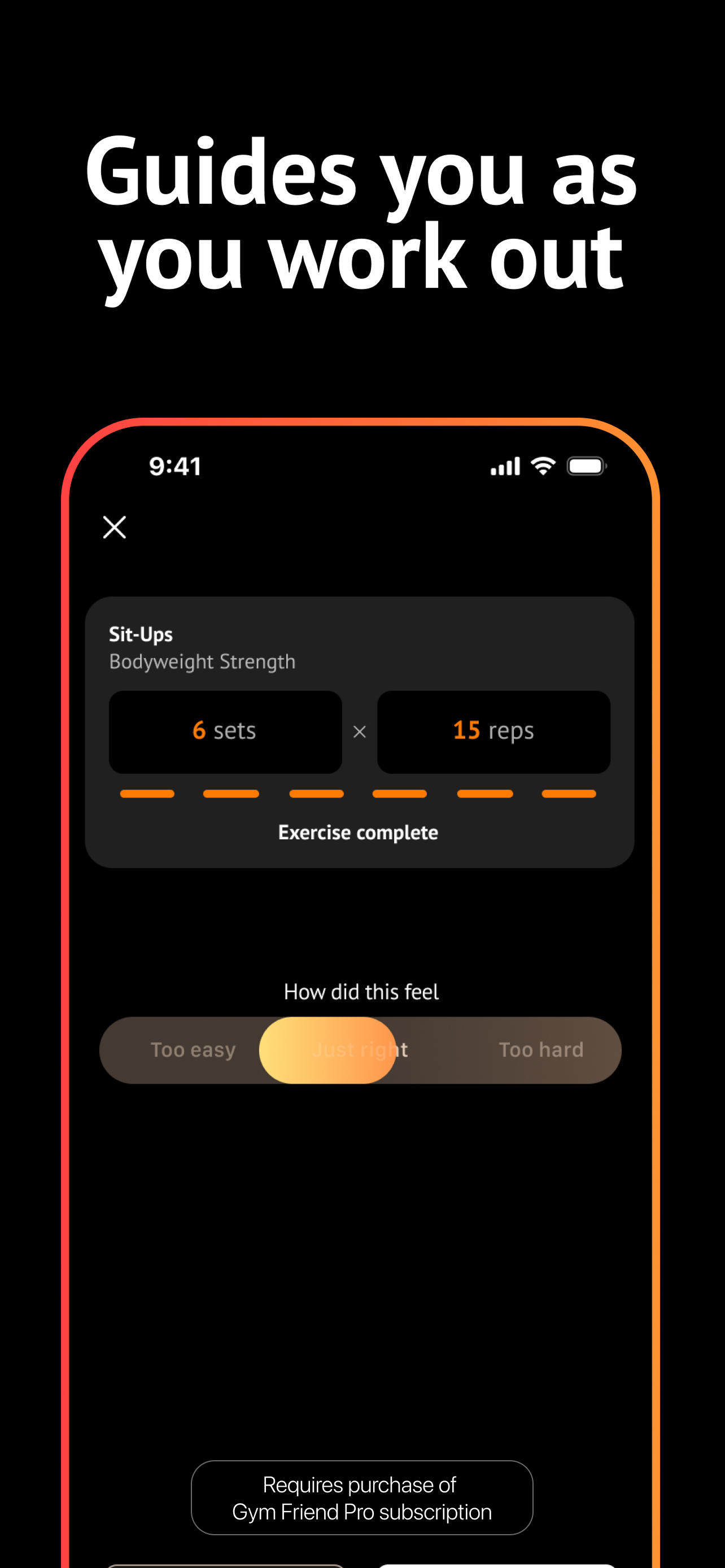
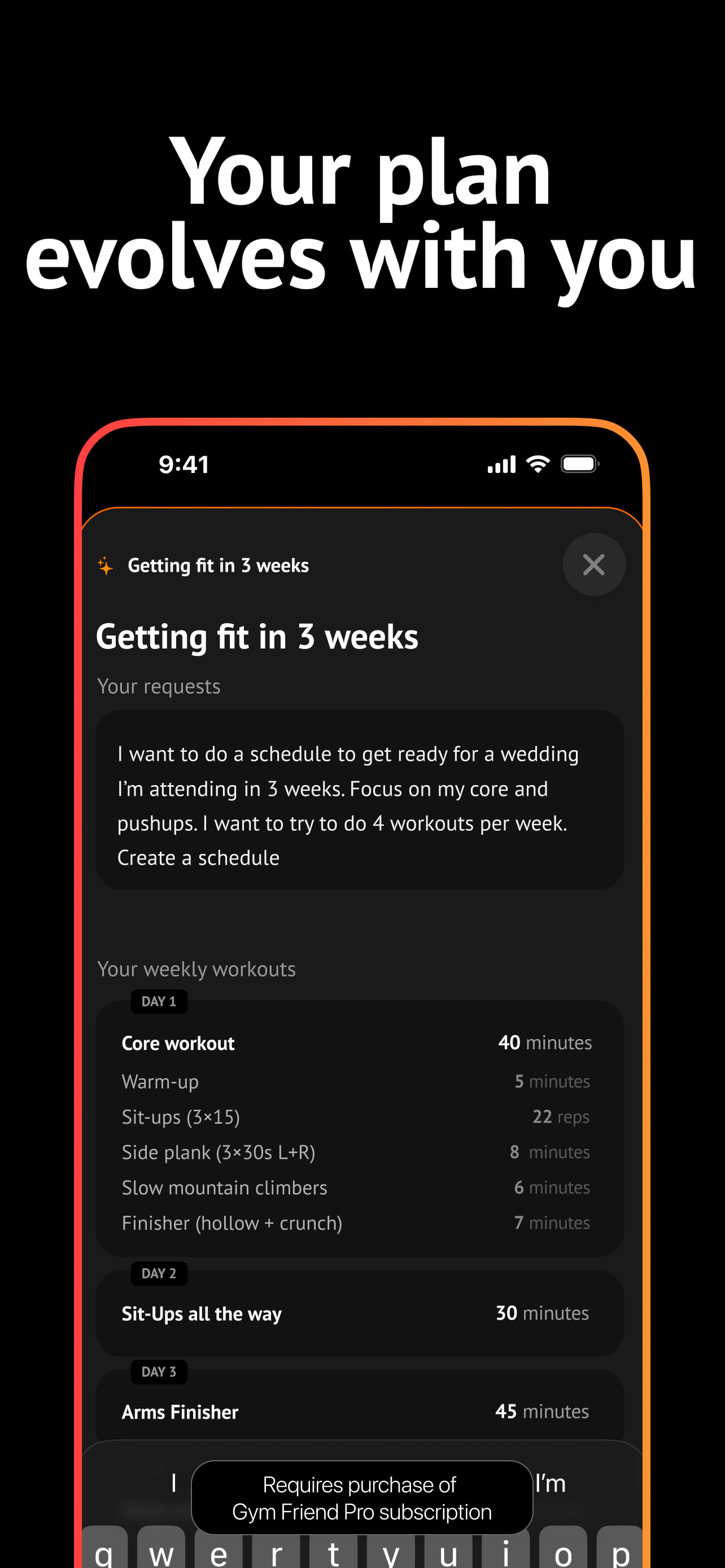
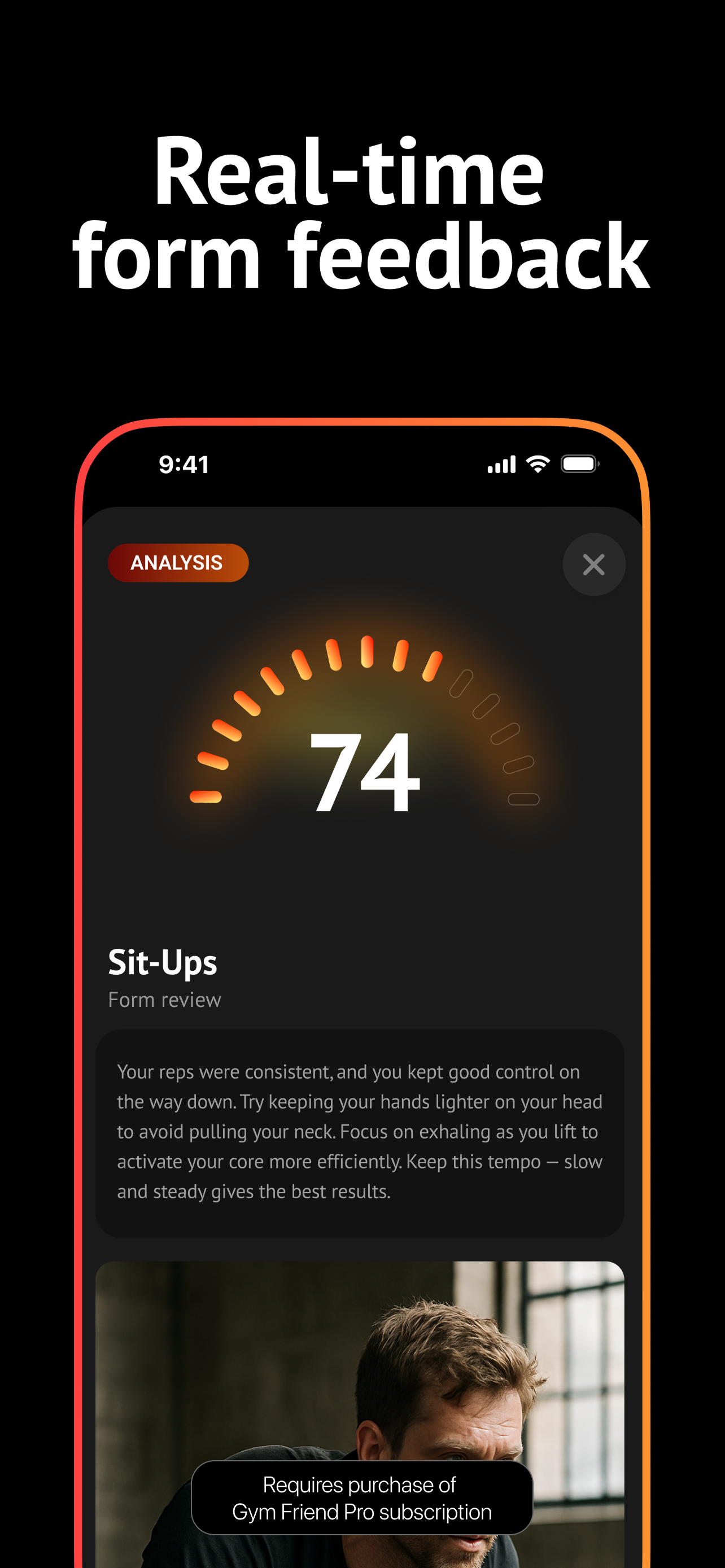
Edit your plan, track progress, and get realtime coaching
Frequently Asked Questions
Should I do cardio too, or just strength training?
Strength training should be your priority, but adding 2-3 low-intensity cardio sessions (like walking) on non-lifting days can accelerate fat loss without compromising recovery. Avoid excessive high-intensity cardio, which can interfere with strength gains.
How much protein do I need when trying to lose weight?
Aim for 0.8-1g of protein per pound of body weight daily. This higher intake helps preserve muscle during a caloric deficit. Spread your protein across 4-5 meals for optimal muscle protein synthesis.
Will I lose muscle if I'm eating fewer calories?
Not if you strength train and eat adequate protein. Research shows that individuals who combine resistance training with a moderate caloric deficit lose primarily fat while maintaining or even gaining muscle.
How many calories does strength training burn?
A typical 45-minute strength session burns 200-400 calories during the workout. But the real magic is the afterburn—your metabolism stays elevated for up to 48 hours, burning hundreds of additional calories.
What if the scale isn't moving?
Don't panic. It's common to lose fat while gaining muscle, which can keep the scale stable while your body composition improves dramatically. Take measurements and progress photos—these tell the real story.
How quickly will I see results?
With consistent training and nutrition, most people notice improved energy and strength within 2 weeks. Visible changes in body composition typically appear at 4-6 weeks. Sustainable fat loss occurs at 0.5-1% of body weight per week.